15. Closing and Guest Lecture
Part of CS231n Winter 2016
Lecture 15: Course Recap and Guest Lecture by Jeff Dean¶
There is no recorded lecture for this session. Instead, we have a recap of the course followed by notes from Jeff Dean's guest lecture.
Course Recap¶
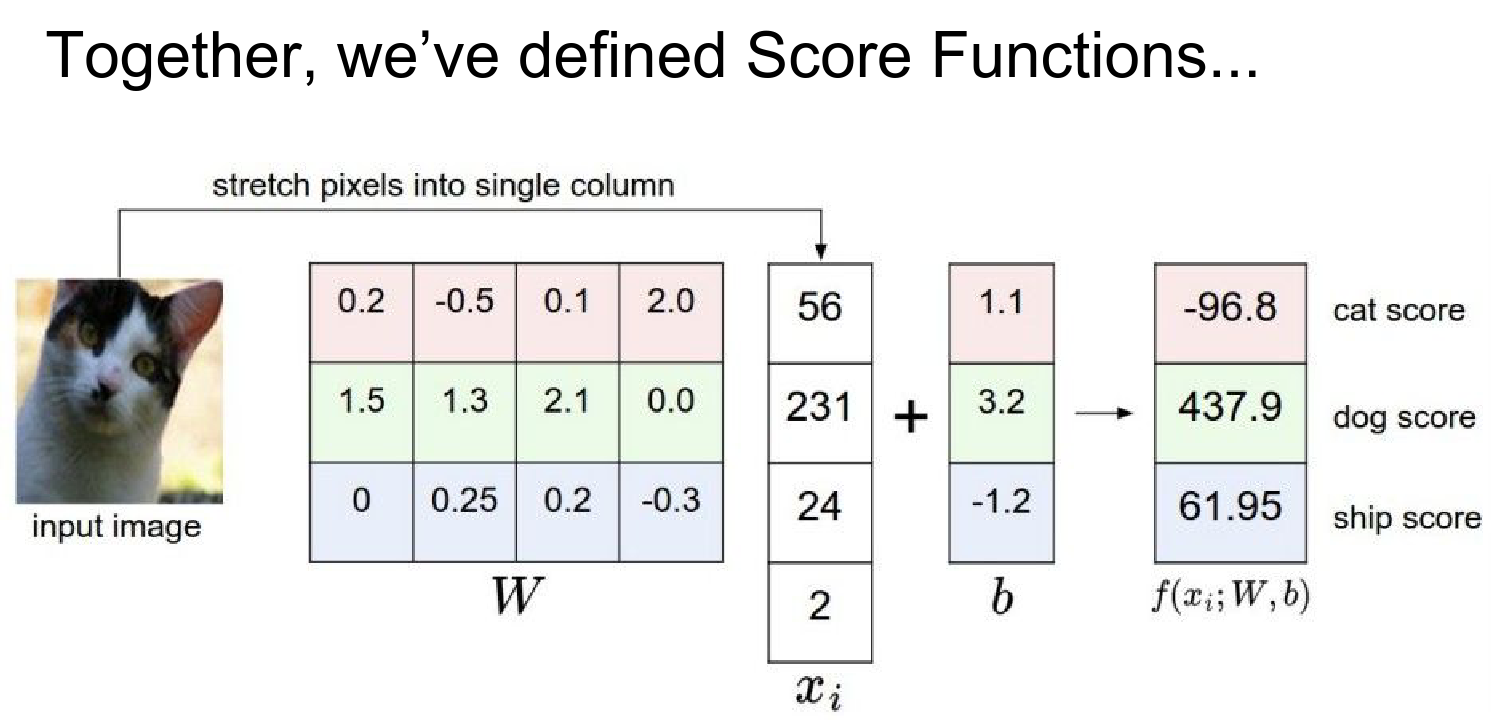
We started by defining Score Functions to map pixels to class scores.
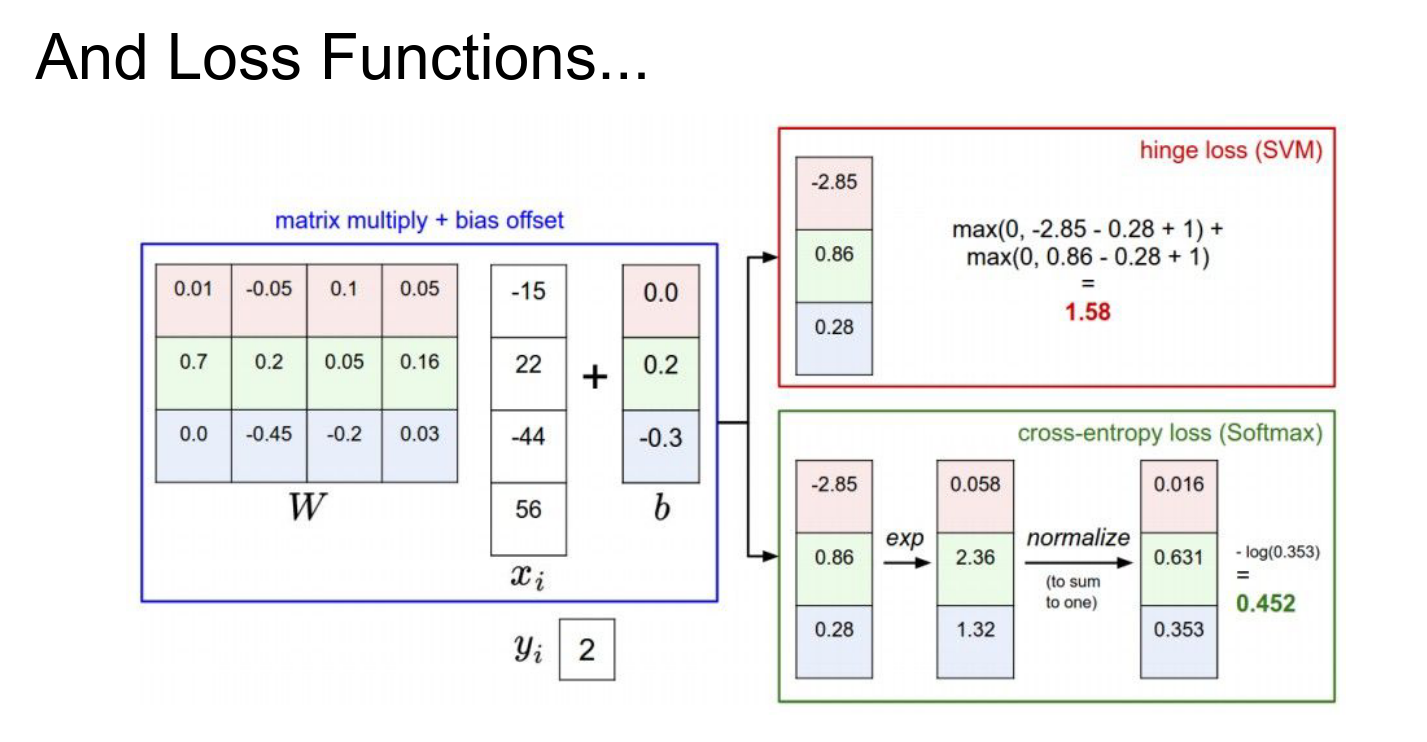
Then we introduced Loss Functions to measure how good our predictions are.
We learned how to optimize these functions using Gradient Descent and backpropagation.

We looked at more powerful linear classifiers and score functions.
We saw that bigger models generally gave us better results.
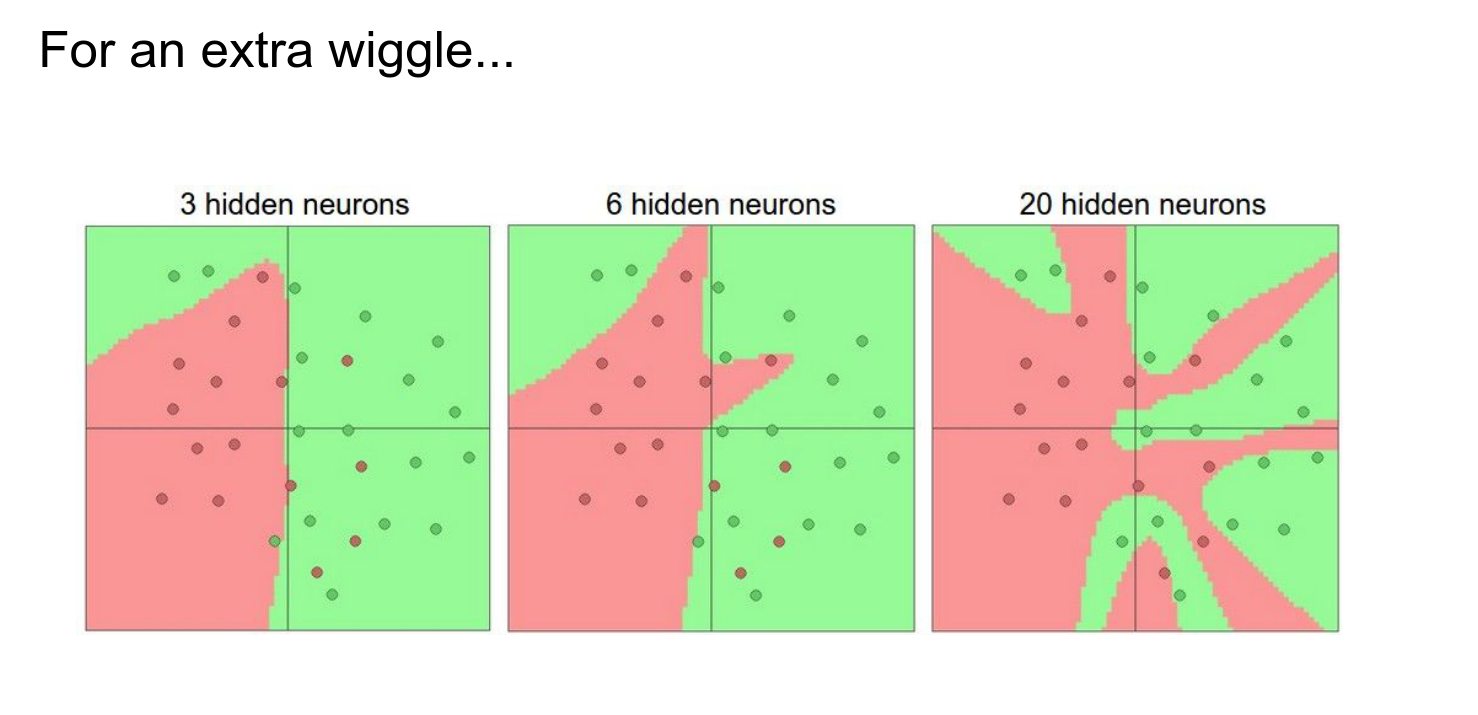
We dove deep into the Learning Process, understanding activation functions, initialization, and regularization.
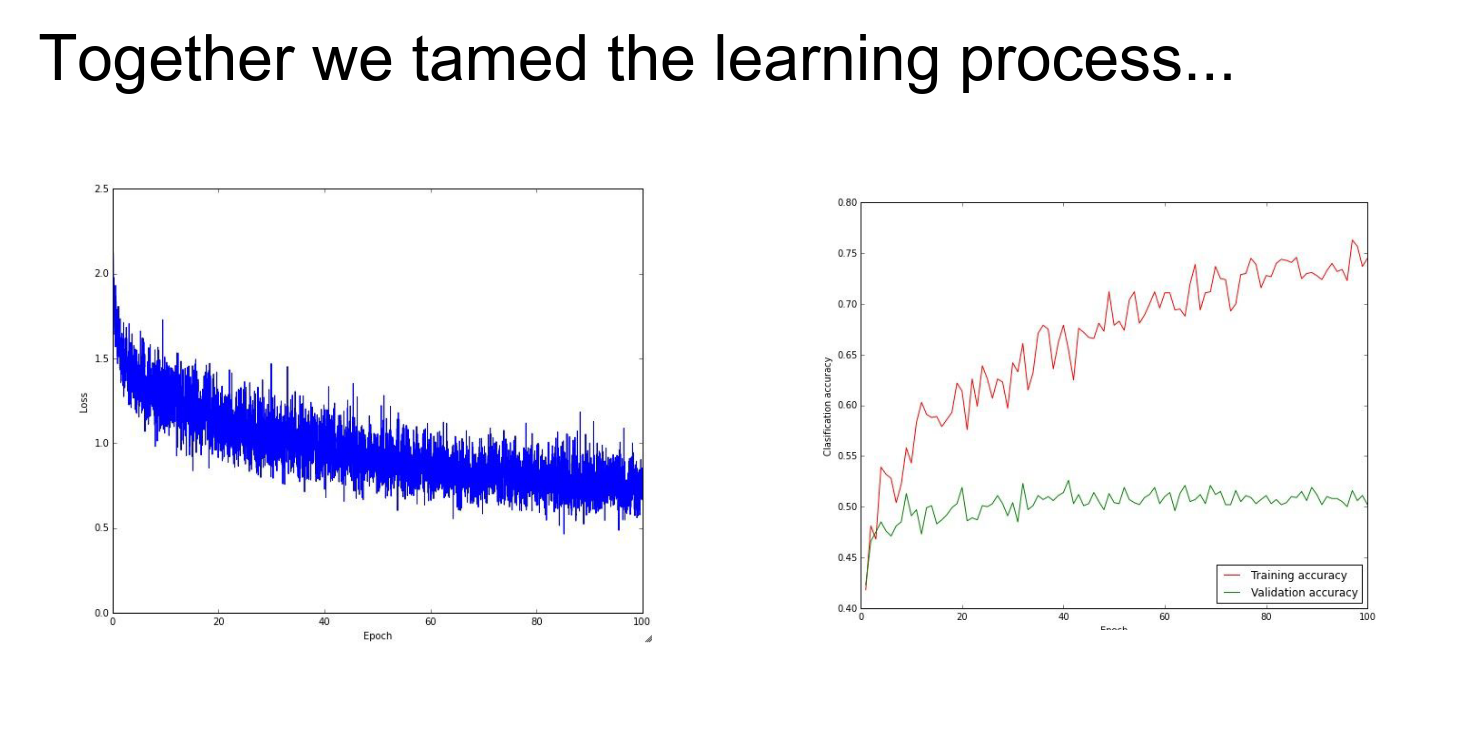
We explored Convolutional Neural Networks (ConvNets), the core of modern computer vision.

We explored them further, looking at standard architectures like AlexNet, VGG, and GoogLeNet.

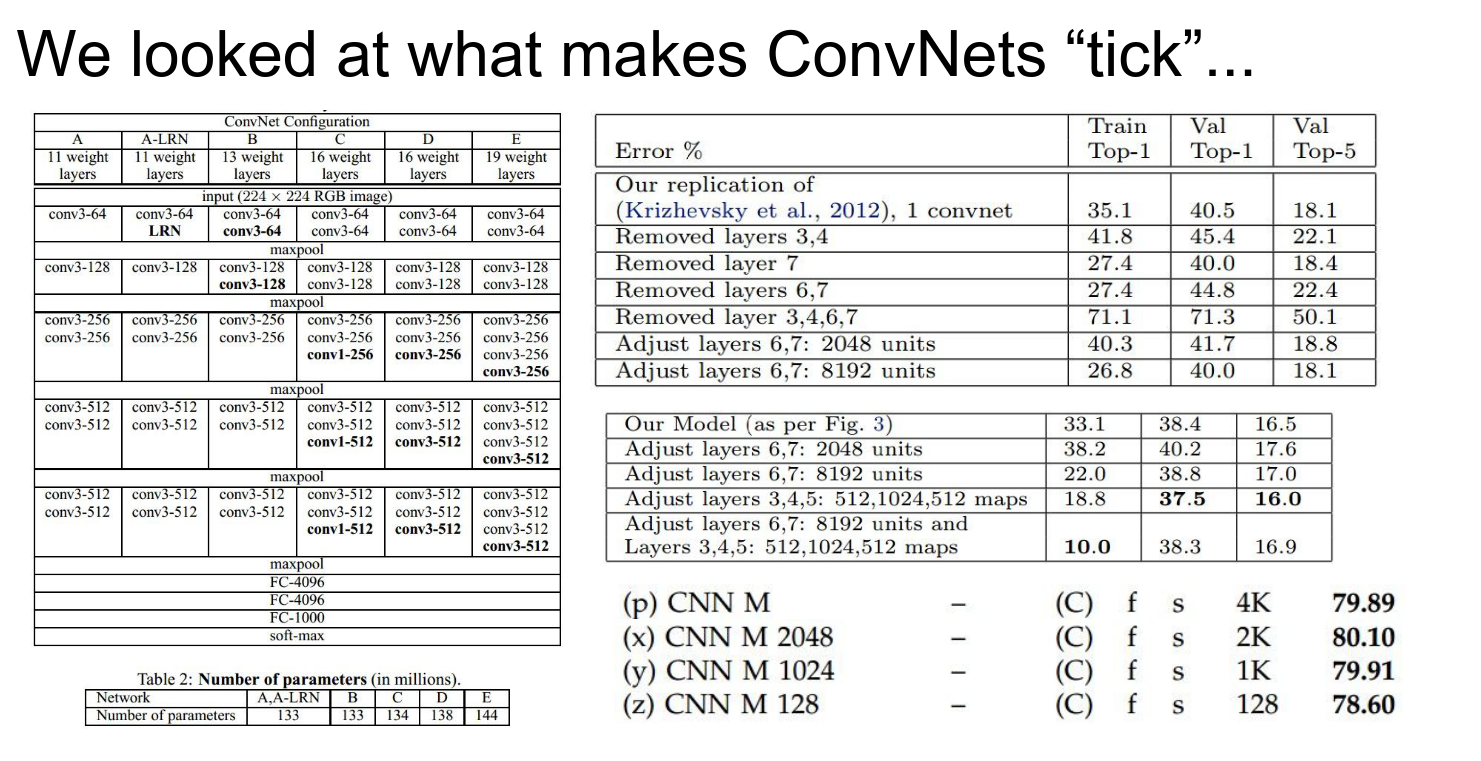
We discussed their potential downfalls and how to visualize what they learn.

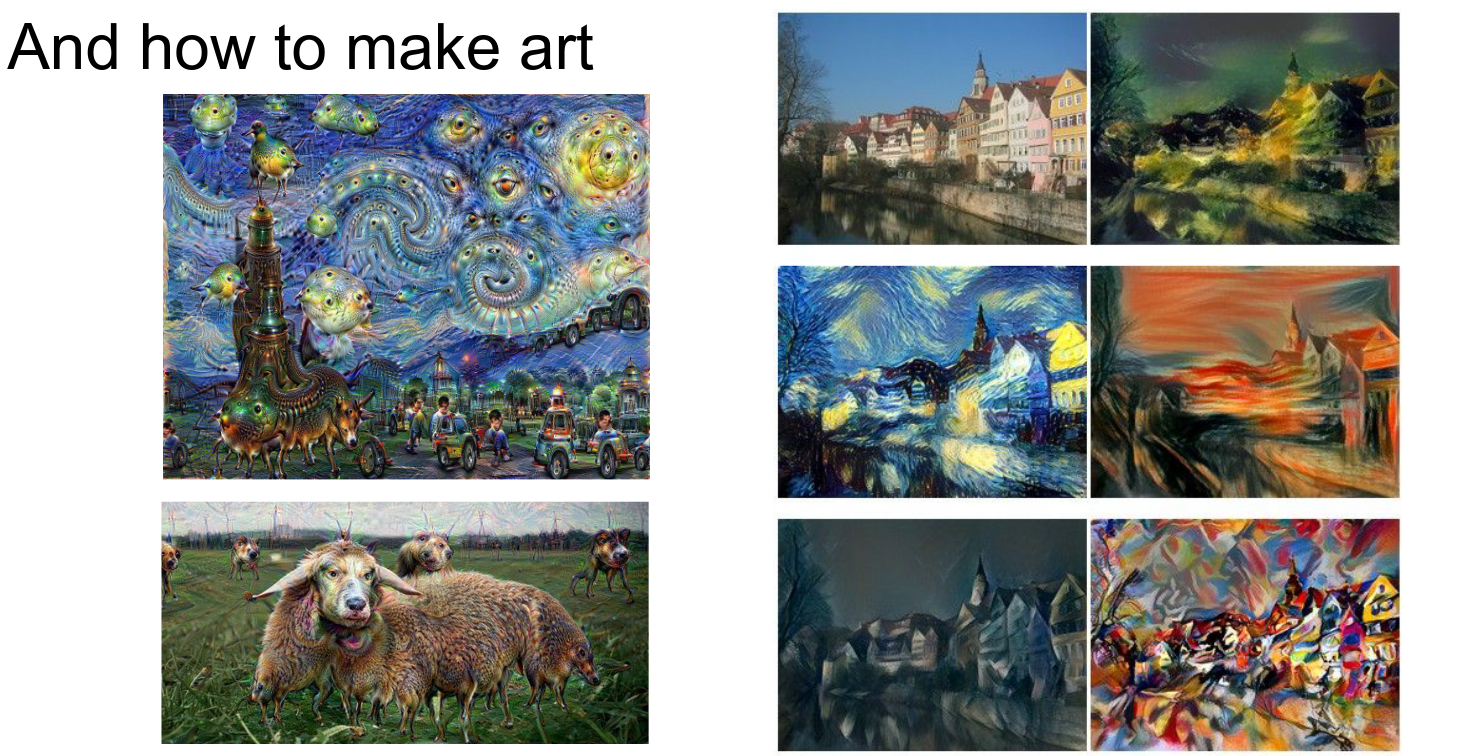
We learned about Style Transfer and generating art with neural nets.

We discovered architectural tricks and newer models like ResNets.
We discussed how to make them work in practice, covering libraries like Caffe, Torch, and TensorFlow.

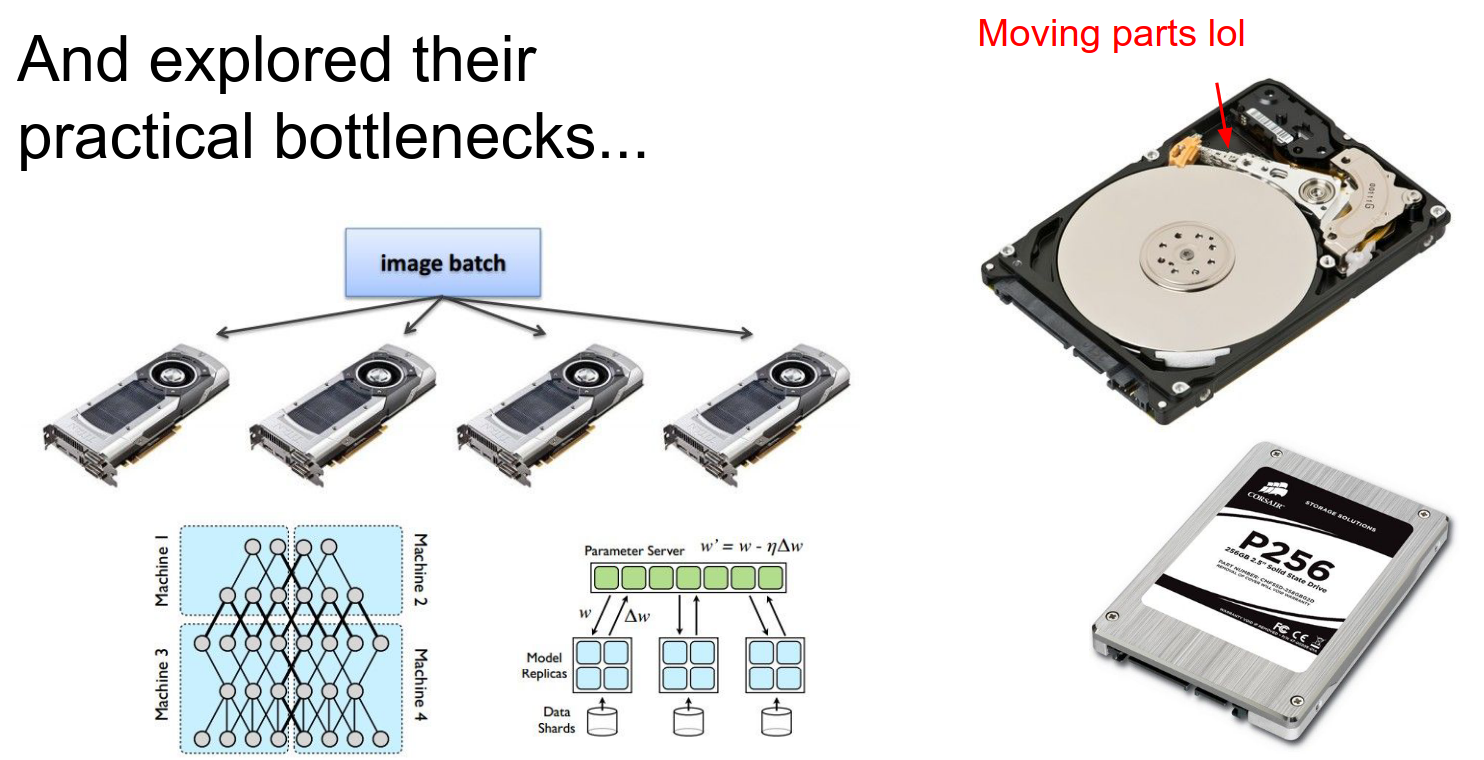
We looked at hardware bottlenecks and implementation details.
We saw that there are many ways to approach classification and detection.
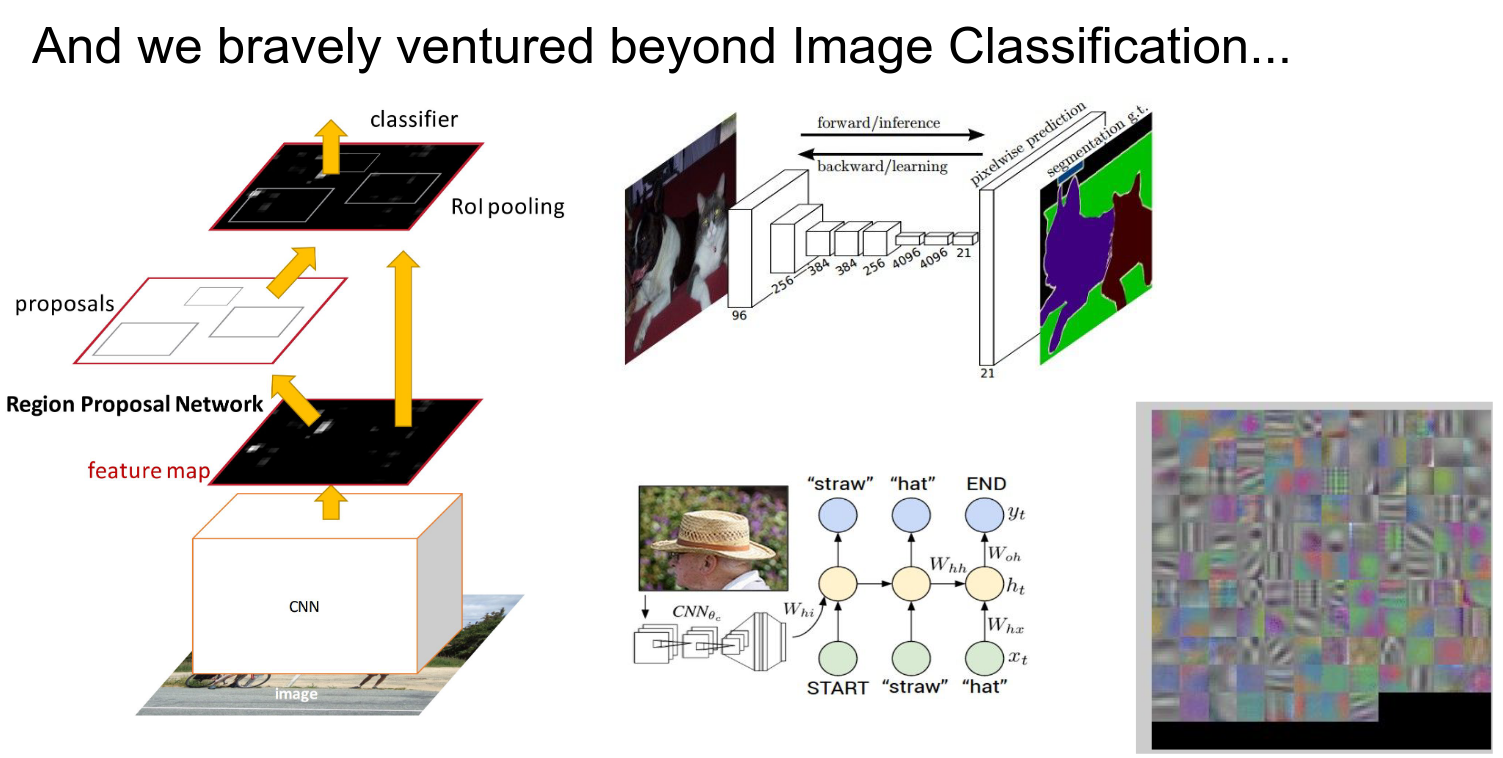
We learned about Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and LSTMs for sequence modeling.

We tackled complex tasks like Image Captioning.

You are now ready.

Go forth and conquer.

The future of computer vision is bright.

The End.

Thank you all!

Guest Lecture: Jeff Dean¶
Jeff Dean gave a guest lecture on large-scale deep learning at Google.
Background:
- Andrew Ng spent a week at Google in 2011, which kickstarted the Google Brain project.
- Google Brain started in 2011.
Research Areas:
- Speech Recognition
- Computer Vision (Images, Videos)
- Robotics
- Language Understanding (NLP, Translation)
- Optimization Algorithms
- Unsupervised Learning
Production Applications:
- Advertising
- Search
- Gmail (Smart Reply, Spam Filtering)
- Google Photos (Search, Organization)
- Google Maps (Street View analysis)
- YouTube (Recommendations, Analysis)
- Speech Recognition (Android, Home)
Key Takeaways:
-
Performance matters: Making models run fast is crucial for both research iteration and production deployment.
-
Scaling: Scaling both Data and Model Size yields significant improvements. Large-scale distributed training is essential.